Robotic Hip Replacement
Robotic hip replacement is a minimally invasive surgical technique designed to replace a damaged hip joint using advanced robotic assistance. This procedure allows for more precise planning and placement of the hip prosthesis, resulting in potentially better outcomes and a quicker recovery. The robotic system enhances the surgeon’s ability to perform the surgery with greater accuracy by providing real-time data during the procedure.
How Common It Is and Who Gets It? (Epidemiology)
Robotic hip replacement is an emerging technology, but its use is increasing steadily as more hospitals and surgical centers incorporate robotic systems. It is primarily used in patients with hip arthritis or other degenerative joint diseases that cause severe pain and limited mobility. The vast majority of patients suffering from hip osteoarthritis are candidates for this type of surgery. However, it is most beneficial in patients with mild to moderate joint degeneration, particularly those who are younger or more active.
Why It Happens – Causes (Etiology and Pathophysiology)
Hip arthritis, including osteoarthritis, is the most common cause for hip replacement surgery. Over time, the cartilage that cushions the hip joint wears away, causing the bones to rub together. This results in pain, swelling, and limited mobility. The precise cause of arthritis may vary, but the most common factors include age, trauma, obesity, and genetic predisposition.
Robotic Hip Replacement Materials and Equipment
The actual implants used in robotic hip replacement surgery are identical to the implants that are used in hip replacement surgeries that are not assisted by a robot. The way the equipment differs is that, rather than have the surgeon make bony cuts by hand using visual estimates, there is a sophisticated computer-navigation software built into the robot that allows the computer to build a 3D picture of the patient’s hip at the time of the surgery, based on information input into it by the surgeon.
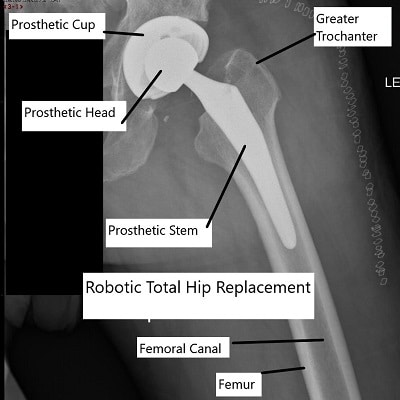
Total hip replacement using robotic assistance.
Once this 3D picture has been constructed, the robot can then calculate the best positions to make the bony cuts necessary to remove the arthritis from the hip. This includes the depths, angle and exact position on the bone of the necessary cuts.
How the Body Part Normally Works? (Relevant Anatomy)
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint composed of the femoral head (ball) and the acetabulum (socket) in the pelvic bone. The femoral head is covered with smooth articular cartilage that allows the bones to glide smoothly against each other during movement. When the cartilage wears down due to arthritis or other conditions, bone-on-bone friction occurs, leading to pain and decreased joint function.
What You Might Feel – Symptoms (Clinical Presentation)
-
Severe pain in the hip, especially when walking, sitting, or getting up from a chair.
-
Stiffness in the hip joint that makes it difficult to move the leg or perform everyday tasks.
-
Swelling or inflammation around the hip.
-
Weakness or reduced mobility in the leg.
-
Grinding or popping sensations when moving the hip.
How Doctors Find the Problem? (Diagnosis and Imaging)
-
Physical Examination: The doctor will assess your range of motion, check for tenderness, and evaluate the function of your hip joint.
-
X-rays: Typically the first step to assess the extent of joint degeneration and the overall condition of the bones.
-
MRI: Provides detailed images of the soft tissues, including cartilage, to assess the extent of damage.
-
CT Scans: Used for more detailed analysis of bone and joint structure, often used for pre-surgical planning with robotic systems.
Procedure Types or Techniques (Classification)
The procedure involves the removal of the damaged femoral head and acetabulum, which are then replaced with prosthetic components. The robotic system provides real-time assistance, ensuring the accurate placement of the implants:
-
Femoral Stem: Inserted into the femur.
-
Acetabular Cup: Inserted into the pelvis.
-
Prosthetic Head: Attached to the femoral stem.
The robotic system assists in determining the precise alignment and positioning of the implants for the best possible outcome.
Other Problems That Can Feel Similar (Differential Diagnosis)
-
Trochanteric Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa on the side of the hip.
-
Sciatica: Pain radiating from the lower back to the hip due to nerve compression.
-
Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease that affects both the hip joint and other joints, such as the knee.
-
Hip Labral Tear: Damage to the cartilage in the hip socket that can cause pain and instability.
Treatment Options
Conservative Treatment: Includes physical therapy, weight management, pain medications, and injections (e.g., corticosteroids).
Surgical Treatment: Robotic hip replacement surgery is recommended when conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
Recovery and What to Expect After Surgery
-
Hospital Stay: Patients typically stay in the hospital for 1-2 days post-surgery.
-
Physical Therapy: Begins the day after surgery to restore movement, strength, and function.
-
Full Recovery: Most patients experience significant pain relief within 2-3 weeks. Full recovery may take up to 6 months, with gradual return to normal activities.
Possible Risks or Side Effects (Complications)
-
Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection.
-
Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can occur post-surgery.
-
Implant Loosening: The prosthetic components can loosen over time, requiring further intervention.
-
Nerve Damage: In rare cases, nerve injury may occur.
-
Dislocation: The hip joint may dislocate if the components are not properly aligned.
Long-Term Outlook (Prognosis)
The long-term prognosis for robotic hip replacement is excellent, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and functional improvement. The prosthetic components can last 15-20 years, and some patients may not need revision surgery for their entire lifetime.
Out-of-Pocket Costs
Medicare
CPT Code 27130 – Robotic Hip Replacement (Total Hip Arthroplasty with Robotic Assistance): $303.45
Medicare Part B typically covers 80% of the approved cost for this procedure once your annual deductible has been met, leaving you responsible for the remaining 20%. Supplemental Insurance plans such as Medigap, AARP, or Blue Cross Blue Shield generally cover that remaining 20%, minimizing or eliminating out-of-pocket expenses for Medicare-approved surgeries. These plans coordinate with Medicare to fill the coverage gap and reduce financial responsibility.
If you have Secondary Insurance, such as TRICARE, an Employer-Based Plan, or Veterans Health Administration coverage, it serves as a secondary payer. These plans generally cover any remaining balance, including coinsurance or small deductibles, which usually range from $100 to $300, depending on your plan and provider network.
Workers’ Compensation
If your robotic hip replacement is required due to a work-related injury or degenerative hip disease caused by your job, Workers’ Compensation will cover all associated medical expenses, including surgery, rehabilitation, and follow-up care. You will not have any out-of-pocket expenses, as the employer’s insurance carrier directly covers all approved treatments.
No-Fault Insurance
If your hip replacement surgery is needed due to an automobile accident, No-Fault Insurance will typically cover the full cost of treatment, including surgery and postoperative care. The only potential out-of-pocket cost may be a small deductible or co-payment depending on your insurance policy.
Example
Emma Clark underwent robotic hip replacement (CPT 27130) for her hip arthritis using robotic assistance. Her estimated Medicare out-of-pocket cost was $303.45. Since Emma had supplemental insurance through Blue Cross Blue Shield, her remaining balance was fully covered, leaving her with no out-of-pocket expenses for the procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. How long will my hip replacement last?
A. With proper care, most hip replacements last 15-20 years or more.
Q. Can I return to sports after robotic hip replacement?
A. Low-impact activities like swimming, biking, and walking are typically encouraged, but high-impact activities like running or jumping are not advised.
Summary and Takeaway
Robotic hip replacement is a highly precise and effective surgical technique that provides accurate implant placement, resulting in improved function and faster recovery. It is suitable for most patients with hip arthritis who meet specific criteria.
Clinical Insight & Recent Findings
A recent study compared robot-assisted posterior total hip replacement with both manual posterior and anterior approaches, finding that robotic assistance improved the precision of leg-length restoration and slightly enhanced functional outcomes compared with the manual posterior method, while showing similar accuracy to the anterior approach.
This supports what surgeons observe in practice — that robotic systems can create a 3D model of the hip and guide bone cuts with greater precision, allowing smaller incisions and more conservative tissue dissection.
Although long-term results are still being studied, current evidence shows that robotic hip replacement offers excellent alignment accuracy without added risk, providing consistent results for patients suffering from advanced hip arthritis. (“Study on robot-assisted total hip replacement – see PubMed.“)
Who Performs This Surgery? (Specialists and Team Involved)
Orthopedic surgeons who specialize in joint replacements typically perform robotic hip replacement surgery. The procedure is supported by a multidisciplinary team, including anesthesiologists, surgical nurses, and physical therapists.
When to See a Specialist?
If you experience persistent hip pain that interferes with daily activities and have not found relief from conservative treatments, consider consulting an orthopedic surgeon.
When to Go to the Emergency Room?
Seek emergency care if you experience sudden, severe pain, swelling, or signs of infection (fever, redness) after hip surgery.
What Recovery Really Looks Like?
Recovery from robotic hip replacement follows a similar path to traditional hip replacement, with pain relief beginning within days and full recovery taking a few months.
What Happens If You Delay Surgery?
Delaying surgery can lead to further joint damage, increased pain, and a longer, more complicated recovery when surgery is eventually performed.
How to Prevent Recurrence or Failure?
Follow post-operative instructions carefully, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid high-impact activities to extend the lifespan of your implant.
Nutrition and Bone or Joint Health
Proper nutrition, including adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, is important for bone health and recovery.
Activity and Lifestyle Modifications
Engage in low-impact activities to maintain joint function and avoid overloading the prosthetic joint.
Do you have more questions?
Can robotic hip replacement surgery correct leg length discrepancies caused by hip arthritis or deformities?
Yes, robotic hip replacement surgery can help correct leg length discrepancies by precisely positioning the implants to restore proper joint alignment and function.
Are there any restrictions on bathing or showering after robotic hip replacement surgery?
Patients can typically shower or bathe as soon as the wound is dry and healed, usually within a few days after surgery. Your surgeon will provide specific instructions on wound care and bathing.
How soon after robotic hip replacement surgery can I return to work?
The timing of return to work after robotic hip replacement surgery depends on factors such as the type of work, recovery progress, and any physical limitations. Desk-based jobs may allow for an earlier return compared to physically demanding occupations.
Will I need to wear compression stockings after robotic hip replacement surgery?
Compression stockings may be recommended after robotic hip replacement surgery to help prevent blood clots and improve circulation in the legs during the recovery period.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have osteoporosis or weak bone density?
Patients with osteoporosis or weak bone density may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but additional measures such as bone grafting or specialized implants may be necessary to ensure implant stability.
How does the risk of dislocation after robotic hip replacement surgery compare to traditional surgery?
The risk of dislocation after robotic hip replacement surgery may be slightly lower compared to traditional surgery due to the precise positioning of the implants and the use of techniques to optimize stability.
Will I need to wear a brace or immobilizer after robotic hip replacement surgery?
The use of a brace or immobilizer after robotic hip replacement surgery depends on factors such as the surgeon’s preference, the patient’s anatomy, and the stability of the implant. Your surgeon will provide guidance on postoperative bracing if needed.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of hip infections or complications?
Patients with a history of hip infections or complications may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but careful preoperative evaluation and management are essential to minimize the risk of recurrence.
Will I need to undergo physical therapy before robotic hip replacement surgery?
Preoperative physical therapy may be recommended to optimize strength, flexibility, and mobility in preparation for robotic hip replacement surgery, especially for patients with existing hip limitations or muscle weakness.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have metal implants from previous surgeries?
Patients with metal implants from previous surgeries may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but additional precautions may be taken to minimize the risk of complications such as metallosis or interference with the robotic system.
How does the recovery experience of robotic hip replacement surgery differ for older patients compared to younger patients?
Older patients may experience a slightly longer recovery period after robotic hip replacement surgery due to factors such as decreased bone density and muscle strength, but outcomes are generally favorable across age groups.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of blood clotting disorders or other medical conditions?
Patients with a history of blood clotting disorders or other medical conditions may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but thorough preoperative evaluation and management are essential to minimize the risk of complications such as thrombosis.
How soon after robotic hip replacement surgery can I resume normal household activities, such as cooking and cleaning?
Patients can typically resume light household activities within a few weeks after robotic hip replacement surgery, but it is important to avoid heavy lifting or strenuous movements until cleared by the surgeon.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of allergic reactions to anesthesia or medications?
Patients with a history of allergic reactions to anesthesia or medications may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but precautions will be taken to minimize the risk of allergic complications during the procedure.
How does the risk of complications such as nerve damage or blood vessel injury compare between robotic hip replacement surgery and traditional surgery?
Robotic hip replacement surgery may have a slightly lower risk of complications such as nerve damage or blood vessel injury compared to traditional surgery due to the enhanced precision and control provided by the robotic system.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a BMI (Body Mass Index) above a certain threshold?
Patients with a BMI above a certain threshold may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but obesity can increase the risk of complications such as infection and implant failure, so weight management may be recommended before surgery.
How does the risk of implant wear and loosening differ between robotic hip replacement surgery and traditional surgery?
Robotic hip replacement surgery aims to optimize implant positioning and stability, potentially reducing the risk of wear and loosening compared to traditional surgery, but long-term outcomes may vary depending on factors such as patient activity level and implant design.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of hip dysplasia or other congenital hip conditions?
Patients with a history of hip dysplasia or other congenital hip conditions may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but careful preoperative planning and assessment of bone structure and alignment are essential for optimal outcomes.
How does the risk of leg length inequality after robotic hip replacement surgery compare to traditional surgery?
Robotic hip replacement surgery aims to minimize leg length inequality by providing precise implant placement and alignment, potentially reducing the risk compared to traditional surgery where alignment may be less accurate.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of chronic pain or fibromyalgia?
Patients with a history of chronic pain or fibromyalgia may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but careful preoperative assessment and management of pain symptoms are important to ensure a successful outcome.
How does the risk of complications such as infection or implant failure change over time after robotic hip replacement surgery?
The risk of complications such as infection or implant failure after robotic hip replacement surgery is generally highest in the immediate postoperative period but decreases over time with proper wound care, rehabilitation, and adherence to postoperative instructions.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of metal sensitivity or allergic reactions to implants?
Patients with a history of metal sensitivity or allergic reactions to implants may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, as alternative implant materials such as ceramic or specialized coatings may be available to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
How does the risk of intraoperative complications such as bone fractures or soft tissue damage compare between robotic hip replacement surgery and traditional surgery?
Robotic hip replacement surgery aims to minimize intraoperative complications such as bone fractures or soft tissue damage by providing real-time feedback and guidance to the surgeon, potentially reducing the risk compared to traditional surgery where visualization and precision may be less precise.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis?
Patients with a history of chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but careful preoperative evaluation and management of disease activity are important to minimize the risk of complications and optimize outcomes.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of hip fractures or trauma to the hip joint?
Patients with a history of hip fractures or trauma to the hip joint may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but careful preoperative assessment and planning are essential to address any existing bone loss or deformity and optimize implant fixation.
How does the risk of complications such as thrombosis or pulmonary embolism differ between robotic hip replacement surgery and traditional surgery?
Robotic hip replacement surgery aims to minimize the risk of complications such as thrombosis or pulmonary embolism by promoting early mobilization and implementing measures to prevent blood clots, potentially reducing the risk compared to traditional surgery where immobility may be prolonged.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of autoimmune diseases or compromised immune function?
Patients with a history of autoimmune diseases or compromised immune function may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but careful preoperative evaluation and coordination with other healthcare providers may be necessary to minimize the risk of complications and optimize outcomes.
How does the risk of complications such as nerve damage or vascular injury differ between robotic hip replacement surgery and traditional surgery?
Robotic hip replacement surgery aims to minimize the risk of complications such as nerve damage or vascular injury by providing enhanced visualization and precision during the procedure, potentially reducing the risk compared to traditional surgery where these structures may be at higher risk of injury.
Can robotic hip replacement surgery be performed if I have a history of neurological conditions or musculoskeletal disorders affecting mobility?
Patients with a history of neurological conditions or musculoskeletal disorders affecting mobility may still be candidates for robotic hip replacement surgery, but careful preoperative assessment and planning are important to address any specific needs or considerations related to mobility and functional outcomes.

Dr. Mo Athar
[et_pb_button admin_label="Button" button_url="https://stage.cortho.org/general-appointment/" url_new_window="off" button_text="Schedule an Appointment" button_alignment="center" background_layout="light" custom_button="on" button_text_color="#FFFFFF" button_bg_color="#02770B" button_border_color="#FFFFFF" button_letter_spacing="1" button_font="Arial" button_on_hover="on" button_text_color_hover="#FFFFFF" button_bg_color_hover="#02770B" button_letter_spacing_hover="1" /]
